Cooler Climate Nova Scotia
Making sparkling wines on the fringe of possibility has its rewards and risks. On the positive side of the equation is world class sparkling wine with ripe grapes at enviable acid levels and moderate sugars. We are right on the cusp of not being able to do what we do, but grapes seem to react to the stresses and reward us with our signature cool climate flavours. It’s been 15 years since planting our estate vineyard with L’Acadie blanc and we have seen remarkable adaptation and resilience to the rigours of a cool climate. And those risks are many – winter damage if temperatures dip below-20C , frosts on either end of the growing season and attaining enough heat units to ripen in our short growing season.
But is our region being affected by global warming? Is it getting easier? That’s a question posed to me recently by a wine writer. My answer: A guarded yes. Yes, when you look at how our climate has warmed over the last 50 years when research scientists at Agriculture Canada in Kentville determined it was too cold in Nova Scotia to support a wine industry. And yes, to the possibilities of vinifera growing here. But our region’s cooler personality can still rear it’s ugly head, like the 2018 spring frost, or described by many as a spring freeze. Temperatures dropped to -2.8C at our estate on June 4 and damaged 80% of our young primary shoots. This was a first for the region’s relatively young grape industry and affected some crops levels severely. We had a second bud burst in late June and those secondary shoots made up for lost time and showed remarkable growth, racing to achieve flowering and verasion at the historical benchmarks and ripening grapes for sparkling wine. An amazing adaptation to a 120 day season compared to our normal 180 frost free days. Crop levels were low, which was beneficial for future growth considering the stresses that the vines endured. We had to adjust distribution for our small production of 2018 still wines and NSLC was accommodating to allow us to restrict their shelf space for a year, so that we could sell direct.
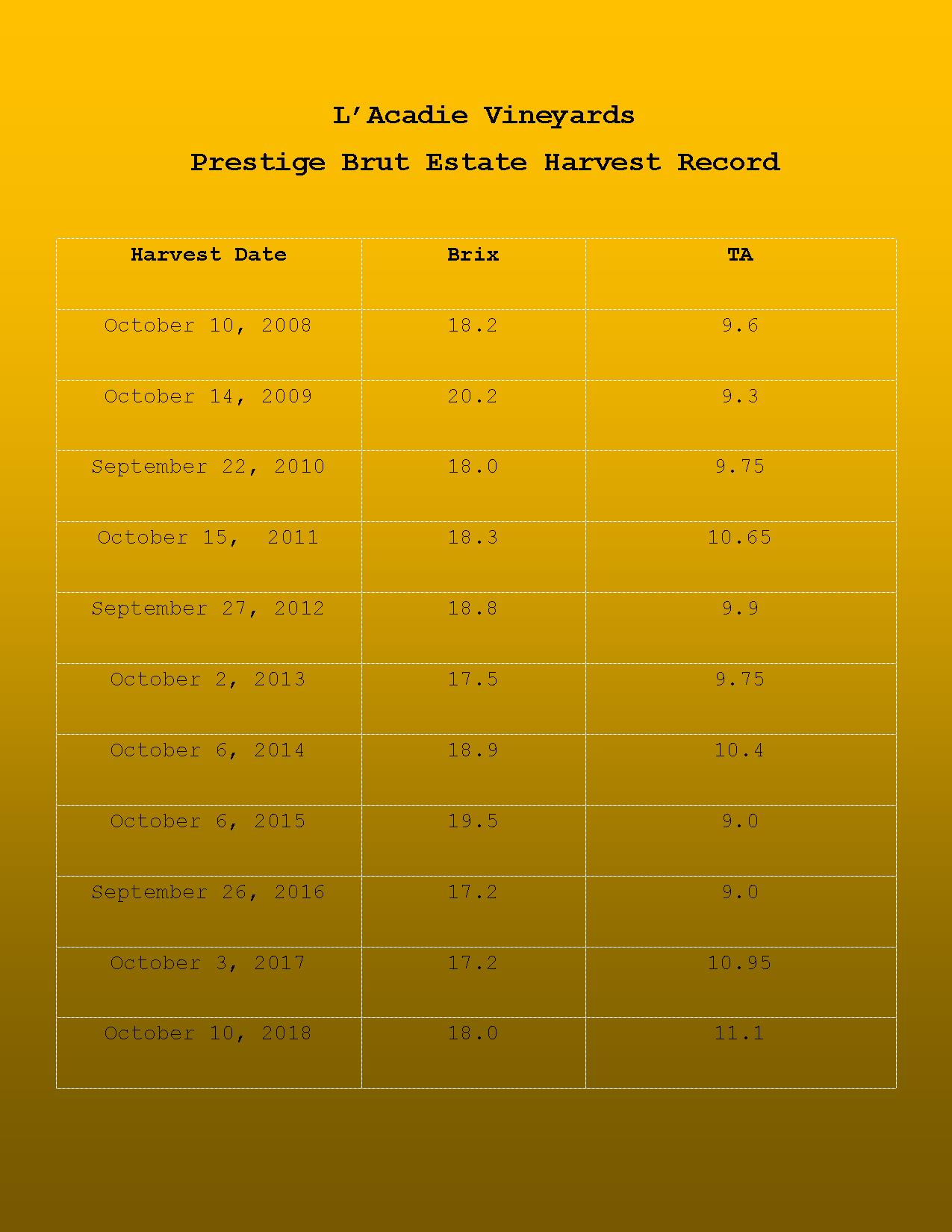
So should we expect more fluctuations in weather, more extreme events? Is that the compromise to the benefits of a warming trend? A look at historical harvest information for sparkling – dates, sugars, acids, is an interesting exercise to see the effects. Champagne has heaps of data for this type of analysis and they have shown that harvest dates have been getting earlier to achieve optimal balance of moderate sugars and enough acidity in their warming climate. I experienced this when I was making sparkling in BC’s Okanagan Valley where the sugar accumulation outpaced ripening in +35C heat and I had to pick before sugars were too high and acid dropped out. But unripe grapes are not ideal for quality sparkling wine and just picking earlier in not always the answer. We’ve had enviable ripeness at our estate for 10 years, including last year. The seeds are lignified, brown, and there are ripe flavours. And harvest dates don’t seem to be trending earlier significantly, as shown in the 10-year harvest record below. And not major fluctuations either. It’s a small sample set compared to Champagne’s 100+ years of data, but significant for our emerging region. Hopefully these enviable quality indicators will continue for many future vintages, in our “cooler climate”.